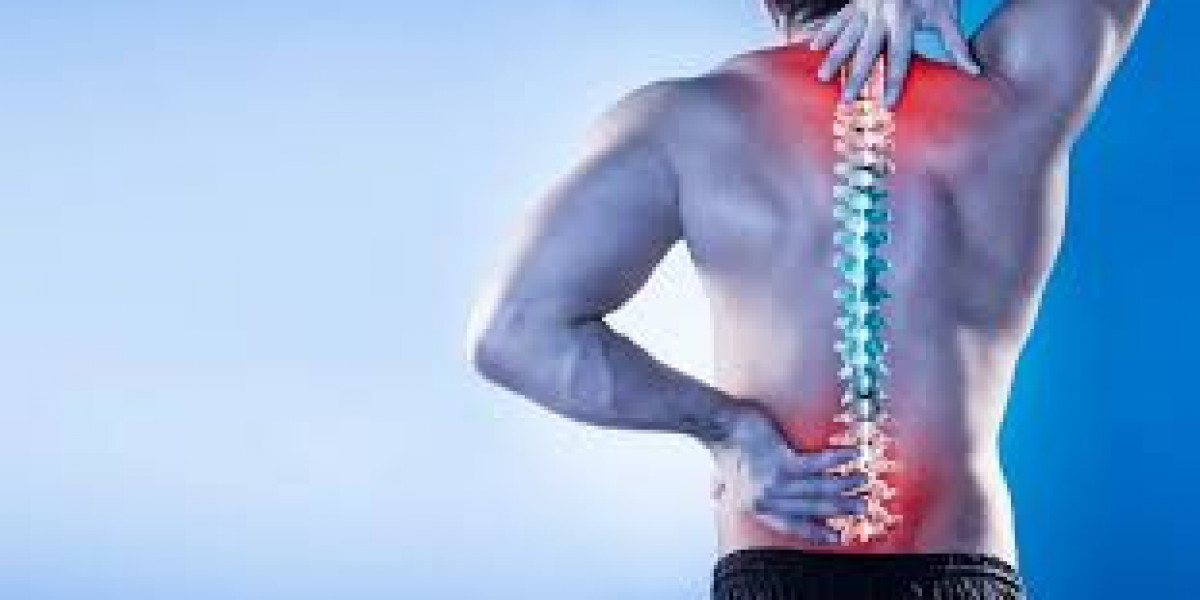
Chronic pain is more than just a prolonged discomfort—it's a complex medical condition that can significantly affect quality of life. For millions of people worldwide, chronic pain is a daily challenge that interferes with work, sleep, and emotional well-being. Understanding what chronic pain is, what causes it, and how it can be managed is essential for both patients and caregivers.
The Etroclas MR tablet belongs to the group of the compounds category- NSAID (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs). It is a combination of the two effective breakthrough formulas- Etoricoxib 60 mg +Thiocolchicoside 40 mg. The medicine is utilized for relieving the patient with the pain taking place due to osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, gouty arthritis, and ankylosing Spondylitis. Also the acute as well as the chronic low back pain along with the muscular spams. This medication is found to be a very effective remedy for providing the relief against the muscle stiffness/ spams, leading to comfort & relief to patient and the improvement in the muscular mobility.
In this blog, we explore the definition of chronic pain, its common causes and symptoms, and the most effective treatment options available today.
What is chronic pain?
Chronic pain is defined as pain that persists for 12 weeks or longer , even after the initial injury or illness has healed. Unlike acute pain, which serves as a warning signal of injury or damage, chronic pain may remain for months—or even years—without a clear purpose.
Chronic pain can be constant or intermittent , mild or severe, and may affect one or multiple parts of the body. It can result from an injury, an underlying health condition, or sometimes occur without an identifiable cause.
Common Causes of Chronic Pain
There are many potential sources of chronic pain. Some of the most common include:
1. Injuries and Trauma
Even after healing, some injuries can lead to ongoing pain due to nerve damage or inflammation. Examples include back injuries, joint sprains, or car accident trauma.
2. Arthritis
Osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis are leading causes of chronic joint pain, especially in older adults.
3. Nerve Damage
Conditions such as neuropathy , sciatica , or shingles (postherpetic neuralgia) can cause chronic nerve pain.
4. Fibromyalgia
This condition causes widespread muscle pain, fatigue, and tenderness without a clear cause. It is often associated with sleep issues and cognitive difficulties.
5. Chronic Illnesses
Conditions like diabetes , cancer , multiple sclerosis , or autoimmune disorders often include chronic pain as a symptom.
6. Back and Neck Conditions
Herniated discs, spinal stenosis, and other musculoskeletal problems frequently result in long-term discomfort.
Symptoms of Chronic Pain
Chronic pain affects more than just the body. It can have far-reaching consequences for mental and emotional health. Common symptoms include:
Persistent or recurring pain (dull, sharp, burning, or throbbing)
Fatigue or low energy
Difficulty sleeping
Mood changes (depression, anxiety, irritability)
Decreased appetite
Limited mobility or stiffness
Cognitive issues, sometimes called “brain fog”
Pain can interfere with day-to-day activities, relationships, and overall quality of life, making comprehensive treatment essential.
Treatment Options for Chronic Pain
Managing chronic pain often requires a multi-disciplinary approach . The right combination of treatments depends on the cause, severity, and how the pain affects your life. Common treatments include:
1. Medications
Over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen or NSAIDs
Prescription medications , such as muscle relaxants, antidepressants, or anticonvulsants for nerve pain
In some cases, opioids may be prescribed, although they are used cautiously due to the risk of dependence
2. Physical Therapy
Regular movement and guided exercise can help strengthen muscles, improve flexibility, and reduce stiffness, especially in back or joint pain.
3. Psychological Support
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), mindfulness, and counseling can help patients manage the emotional effects of chronic pain and improve coping strategies.
4. Interventional Treatments
These may include nerve blocks , injections , radiofrequency ablation , or implanted devices like spinal cord stimulators.
5. Alternative Therapies
Acupuncture, chiropractic care, massage therapy, and yoga are sometimes used as complementary approaches to pain management.
Final Thoughts
Chronic pain is a real and often misunderstood condition that requires understanding, patience, and a well-rounded treatment strategy. If you or someone you know is living with chronic pain, it's important to seek professional help and not suffer in silence. With the right approach, many people can regain control over their lives and find meaningful relief.
Whether through medication, therapy, lifestyle changes, or a combination of treatments, chronic pain can be managed—and life can improve .